Anxiety and Heart Attack
How Nervousness Leads to Heart Attack
13 JUN 2023
Anxiety is a widespread condition that affects people experiencing fear, worry, and nervousness. Although anxiety is often manageable and temporary, prolonged anxiety can have severe health consequences, including heart attacks.
A heart attack occurs when blood transmission is obstructed in the arteries, causing damage to the heart muscle. It is a life-threatening condition that needs immediate medical attention. Let’s explore what happens in a heart attack and how anxiety can lead to it.
What Happens in a Heart Attack?
The heart muscle requires a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients carried to it by the blood. When the blood flow gets obstructed, the heart muscle doesn’t receive enough oxygen and nutrients, causing it to begin dying.
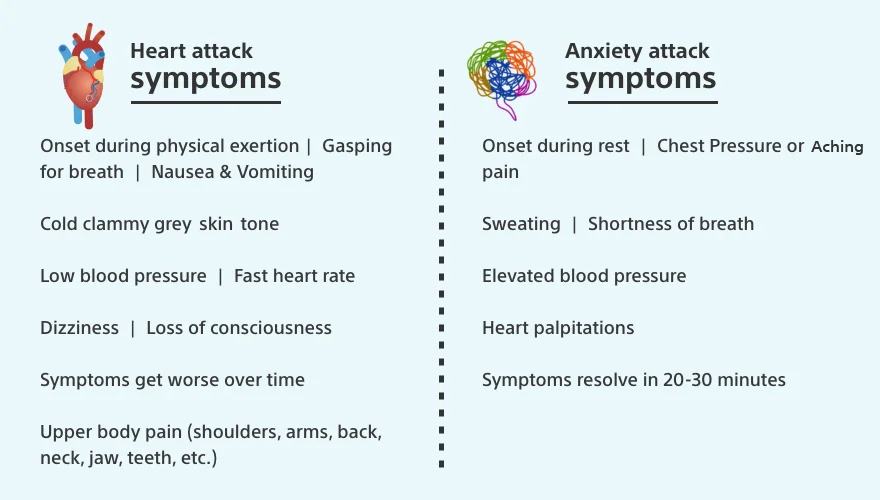
Symptoms of a heart attack can vary, but common symptoms require chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, light-headedness, nausea, and sweating. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
How Anxiety Leads to Heart Attack?
Anxiety can have several physical and emotional effects on the body, including increased heart rate and blood pressure, constricting blood vessels, and elevated stress hormone levels such as adrenaline and cortisol. These effects can strain the heart and increase the risk of a heart attack.
One of the primary ways anxiety can lead to a heart attack is through the constriction of blood vessels. When feeling anxious, the body releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, causing blood vessels to constrict, increasing blood pressure, and decreasing blood flow to the heart. Over time, repeated blood vessel constriction can damage the endothelium, and the blood vessel’s inner lining, causing blood clots to form, blocking blood flow to the heart and leading to a heart attack.
Anxiety elevates stress hormone levels, such as adrenaline and cortisol, as these cause the heart to beat faster and harder, straining the heart muscle. Prolonged exposure to stress hormones can weaken the heart muscle and increase the risk of a heart attack.
Besides physical effects, anxiety can also have emotional effects that increase the risk of a heart attack. For example, stress can cause depression, a risk factor for heart disease. Anxiety can also lead to unhealthy behaviours such as smoking and overeating, increasing the risk of heart disease.
How to Manage Anxiety to Prevent Heart Attack?
Managing anxiety is crucial to prevent heart attacks. Specific strategies can help you manage stress:
- Exercise regularly: Exercise can help reduce anxiety and improve cardiovascular health.
- Practice relaxation techniques: The techniques such as deep breathing and meditation can help reduce anxiety and stress.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep is crucial for overall mental health.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet can help reduce anxiety and improve cardiovascular health.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: It’s essential to stop smoking and excessive alcohol consumption as it will reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Seek professional help: If your anxiety is persistent and interferes with your daily life, seek professional help from a mental health professional.
Exercise regularly
Practice relaxation techniques
Lift chin check breathing
Eat a healthy diet
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
Seek professional help
In addition to these strategies, it is essential to identify and address anxiety. This may involve lifestyle changes such as reducing stress at work or addressing relationship issues. Depending on the severity of the fear, it may also involve therapy or medication. Understanding heart attack symptoms and providing medical attention if you experience any of those is also essential.
Conclusion
Anxiety is a severe condition that can significantly impact mental and physical health. When left unmanaged, anxiety can increase the risk of a heart attack, a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention. It is essential to manage anxiety through exercise, relaxation techniques, and seeking professional help when necessary to reduce the risk of a heart attack. By understanding the connection between anxiety and heart health, we can take proactive steps to protect our well-being and live fulfilling lives.
Disclaimer: The information presented by Boston Scientific India is for educational purposes only and does not recommend self-management of health issues. The information should not be treated as comprehensive and does not intend to provide diagnosis, treatment or any medical advice. Individual results may vary and hence, it is advisable to consult your doctor regarding any medical or health related diagnosis or treatment options.
IC-1566901-0323
Related Articles
Tags
Heart Attack | What happens in Heart Attack | Anxiety | Anxiety Attack Symptoms| Risk Of Heart Disease