When Does A Person Require a Heart Stent? A Quick Insight
When Does A Person Require a Heart Stent? A Quick Insight
03 August 2023
Heart disease is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition affecting millions worldwide. One of the treatments for heart disease is using a heart stent, a small metal or plastic tube inserted into a blocked or narrowed artery to keep it open and improve blood flow to the heart. This blog will discuss when one might require a heart stent, why it is necessary, and how it is used to treat a heart attack.
There are several reasons why a heart stent might be required. Firstly, suppose a patient is experiencing symptoms of coronary artery disease, such as chest pain or shortness of breath. In that case, their doctor may recommend a coronary angiogram to determine the extent of the blockages in their arteries. If the blockages are severe enough, a heart stent may be necessary to open up the artery and improve blood flow to the heart.
Another reason a heart stent might be required is if a patient has already suffered a heart attack. In this case, the stent may open up the blocked artery and restore blood flow to the heart muscle. This can help to reduce the damage caused by the heart attack and improve the patient’s chances of full recovery.
So, why is a heart stent necessary? The main reason is to improve blood flow to the heart and reduce the risk of a heart attack. When an artery becomes blocked or narrowed, the heart muscle may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, which can lead to chest pain or a heart attack. By inserting a stent to keep the artery open, blood flow is restored, and the heart can function more effectively.
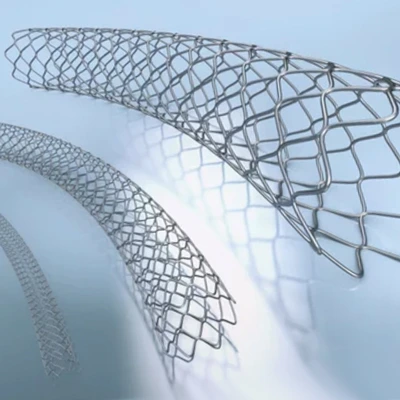
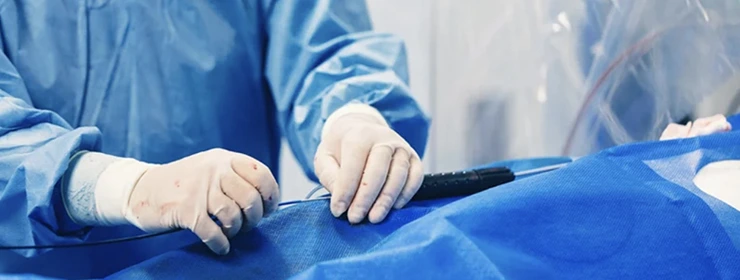
Heart stents are typically made of metal or polymer and are inserted into the blocked artery using a catheter, a thin tube that is threaded through the blood vessels to the affected area. Once the stent is in place, it is expanded to open up the blocked area and then left in place to keep the artery open.
While heart stents are generally safe and effective, some risks are associated with the procedure. These can include:
- Bleeding
- Damage to artery or surrounding tissue
- Infection
- Stent may become blocked
If you are experiencing symptoms of coronary artery disease or have already suffered a heart attack, seeking medical attention as soon as possible is essential. Your doctor can thoroughly evaluate and determine whether a heart stent may be necessary to improve your condition. By working closely with your healthcare team, you can receive the best possible care and reduce your risk of complications.
Disclaimer: The information presented by Boston Scientific India is for educational purposes only and does not recommend self-management of health issues. The information should not be treated as comprehensive and does not intend to provide diagnosis, treatment or any medical advice. Individual results may vary and hence, it is advisable to consult your doctor regarding any medical or health related diagnosis or treatment options.
IC-1600913AA-0523
Related Articles
Tags
Heart Stent | Angina | Chest Pain | Risk of Heart Attack | Coronary Artery Disease | Symptoms and Precautions